Concept
The concept of MRules business rule engine is simple:
- Input Java beans are provided.
- Data is read from these beans and Conditions are evaluated.
- Data is writen into output Java beans.
- An internal caching system allows to avoid several retrievals of the same data from input beans or multiple evaluations of the same condition.
Addon-oriented conception
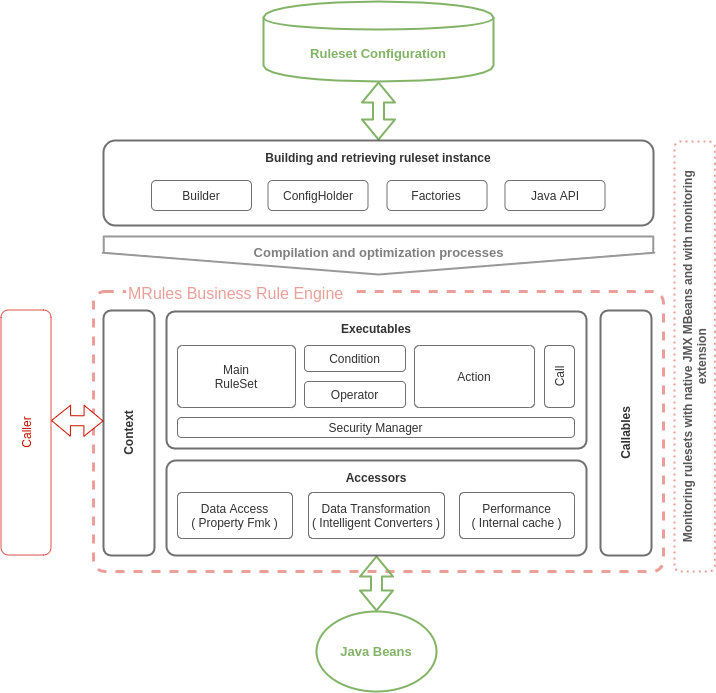
MRules in concieved to be modular and easily extensible. To achive this ambitious goal, an Addon-based structure has been created. Every component of the library is an Addon. It’s so just easy as a pie to add a new feature and to write extensions, which will be dynamically loaded at runtime with very few lines of configuration.
This allows to easily add specific operations in case of a very particular need, although many operations are already possible.
Components
The whole library contains lots of components, which we can classify in different types, depending on their responsability.
- Accessors are responsible of data access (read and write).
- Conditions evaluate data to branch execution.
- Evaluation Operators perform a single data evaluation.
- Logical Operators combine multiple single evaluations.
- Executables (also named “Rules”) are responsible of performing actions and coordinating their execution.
- Actions are special Executable which perform unitary actions (like for instance setting a value).
- The special Executable “Rule Execution Set” is the main root component of a rule set instance.
- Callables are special components which can be invoked any time during execution (for example, functions).
- Builder and Factories read and write rule engine configuration and build rule set instances.
- The contexts allow to launch compilation and execution.
- More information about the security management can be found on the dedicated page.
- More information about rulesets monitoring can be found on the dedicated page.
 Java Business Rule Engine (BRMS)
Java Business Rule Engine (BRMS)